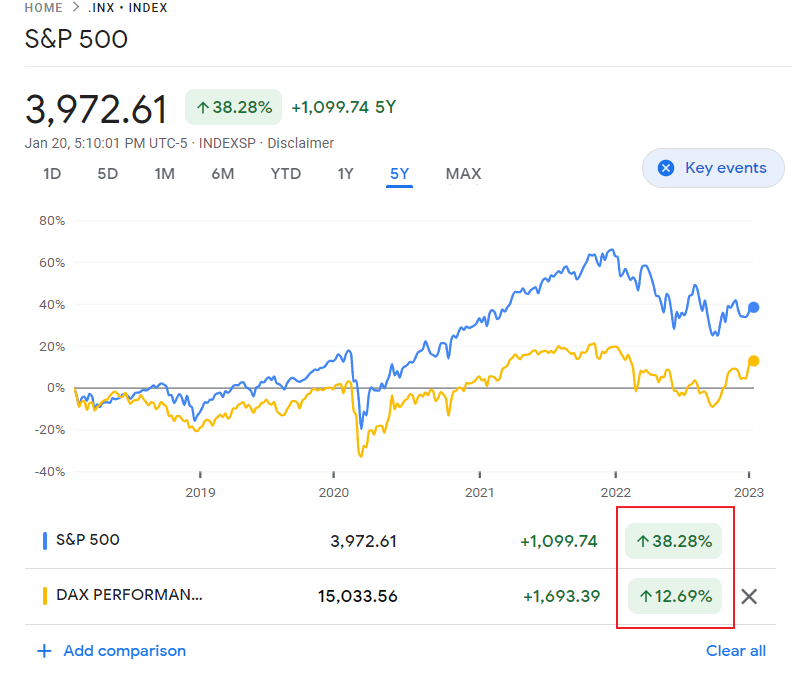
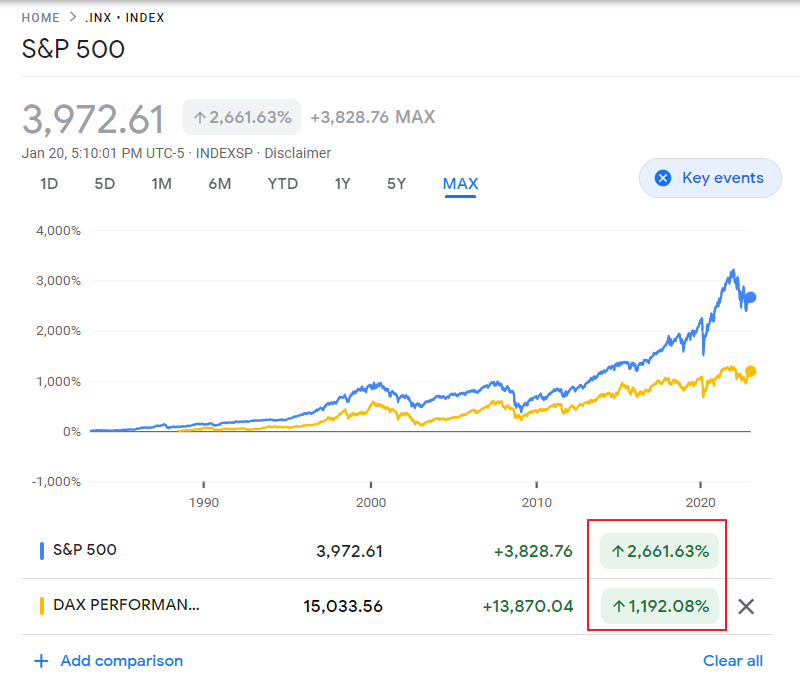
The Dividend Withholding Tax rate for foreign investors in Chilean equities used to be 35%. This rate has been reduced to 23.9041123%. This is a welcome news for ADR holders.
Below is the YTD returns of Chilean ADRs trading on the US exchanges:
Click to enlarge
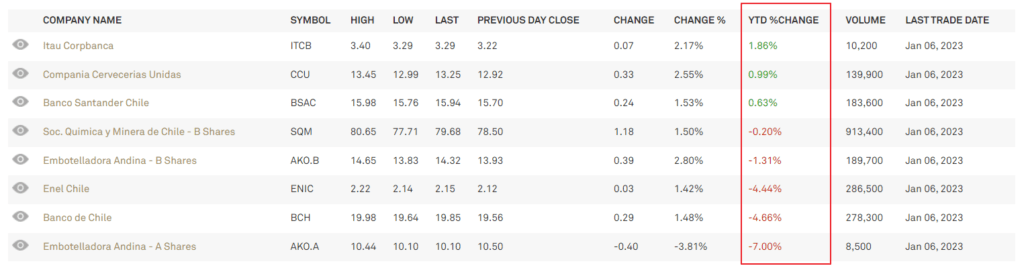
Source: BNY Mellon
Last year Lithium miner Soc. Quimica y Minera de Chile (SQM) had an astonishing run. It remains to be seen if this year also will be great for SQM investors.
Disclosure: Long BCH