Investing in dividend stocks is a wise strategy for many reasons including the fact that dividends alone account for one-third of the S&P 500’s Total Return from 1960 to 2019. So though the dividend yield is small for most US stocks relative to other developed markets they are still important from a long-term wealth building perspective. I came across an interesting study titled “The Importance of Dividends to Total Returns“. by Job Curtis and Neil Hermon at Janus Henderson. Below is an excerpt from the research:
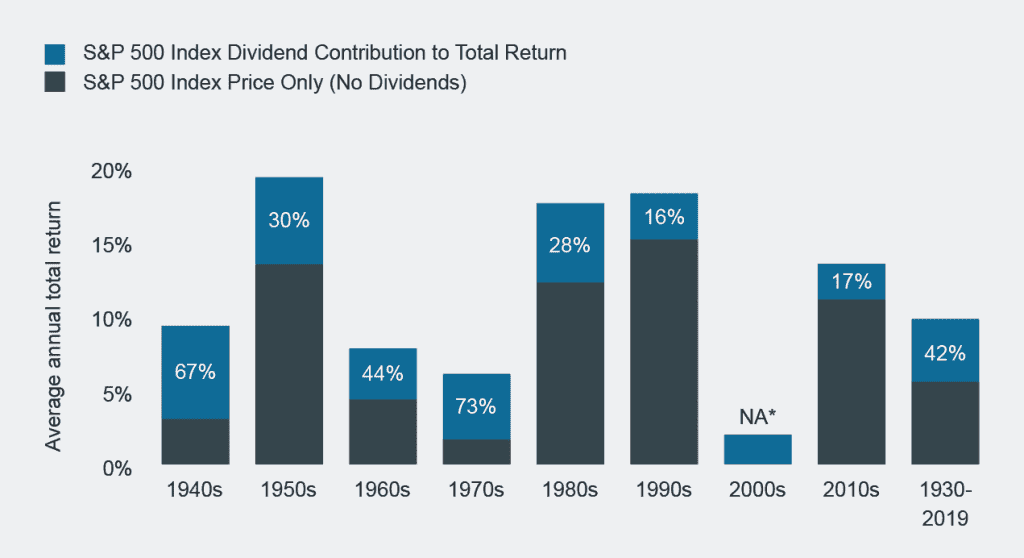
The contribution of dividends to total returns fluctuates over time of course. The analysis below of the widely-followed US large cap barometer, the Standard & Poors 500 Index (S&P 500) from 1930 to 2019, conducted by US-based asset manager Hartford Funds, shows that for the period as a whole, the divided contribution averaged 42% which equates to 1.8% per annum on an annualised basis. Looking at the decades discretely, however, illustrates the extent to which that contribution to total return varies.
Source: Morningstar/Hartford Funds, 02/2020. S&P 500 Index is a market capitalisation weighted price index composed of 500 widely held shares. *Total return for the S&P 500 Index was negative for the 2000s. Dividends provided a 1.8% annualised return over the decade.
During the 1940s, ’60s and ’70s – decades in which total returns were lower than 10% – dividends played a significant role in terms of their contribution, but played a smaller role during the 1950s, ’80s and ’90s when total returns were well into double figures.
During the 1990s, dividends were de-emphasised as companies chose to deploy capital by reinvesting into their businesses rather than by returning it to shareholders. From 2000 to 2009, a period commonly referred to as ‘the lost decade’[3], the S&P 500 delivered a negative return, primarily a consequence of the bursting of the dotcom bubble in March 2000.
[3] Source: S&P 500 Index
Source: The Importance of Dividends to Total Returns, Janus Henderson
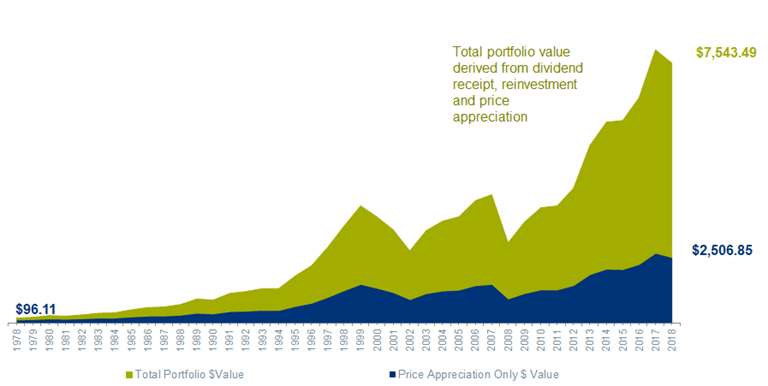
The following is a neat illustration of the above topic for a hypothetical investment from 1978 to 2018:
Click to enlarge
Source: Merits of Dividends, ThomasPartners
From the above article:
To total returns over time.
The ability to reinvest dividends has had a significant impact on an investor’s ability to create wealth in the stock market.
For example, if an investor had purchased one theoretical share of the S&P500 index on December 31, 1978, it would have cost them about $96.11. 40 years later, on December 31, 2018, that one share of the S&P500 would have appreciated to nearly $2,506.85 If the investor had been able to reinvest those dividends in the index, their investment would have grown to over $7,500.
Investors interested in adding dividend payers to their portfolios can consider the below stocks for further research:
1.Company: Exelon Corporation (EXC)
Current Dividend Yield: 3.62%
Industry: Electric Utilities
2.Company: Royal Bank of Canada (RY)
Current Dividend Yield: 4.06%
Sector: Banking
3.Company: Union Pacific Corp (UNP)
Current Dividend Yield: 1.82%
Sector: Railroads
4.Company: Kimberly-Clark Corp (KMB)
Current Dividend Yield: 3.45%
Sector: Household Products
5.Company: Bancolombia SA . (CIB)
Current Dividend Yield: 4.17%
Sector: Banking
6.Company:Colgate-Palmolive Co (CL)
Current Dividend Yield: 2.24%
Sector: Household Products
7.Company: Enbridge Inc (ENB)
Current Dividend Yield: 7.61%
Sector: Oil & Gas Transportation
8.Company: National Grid PLC (NGG)
Current Dividend Yield: 5.30%
Sector: Multi-Utilities
9.Company: Duke Energy Corp (DUK)
Current Dividend Yield: 4.30%
Industry: Electric Utilities
10.Company: The Hershey Company (HSY)
Current Dividend Yield: 2.12%
Industry: Food Products
Dividend Withholding Tax: RY, CIB, ENB, NGG are foreign stocks. Hence the dividend withholding taxes may reduce the yield quoted above. The applicable rate can be found here. On top of this, ADR fees may also be applied.
Note: Dividend yields noted above are as of Feb 16, 2021. Data is known to be accurate from sources used. Please use your own due diligence before making any investment decisions.
Disclosure: Long UNP and RY
Related ETFs:
- SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY)
- iShares Select Dividend ETF (DVY)
- Vanguard High Dividend Yield ETF (VYM)
- Vanguard Dividend Appreciation ETF (VIG)
Disclosure: No Positions