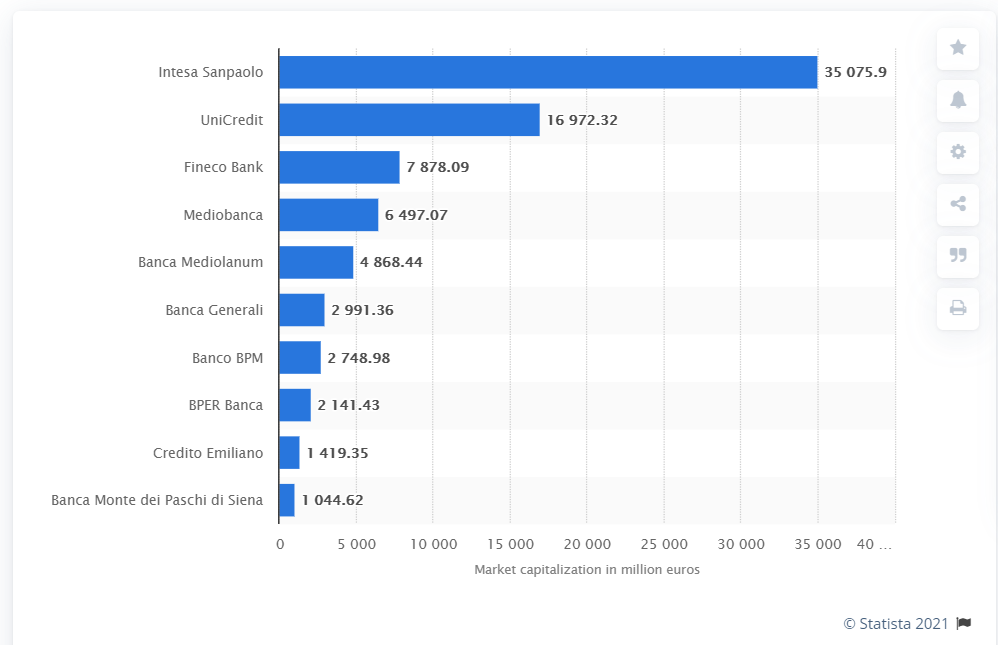
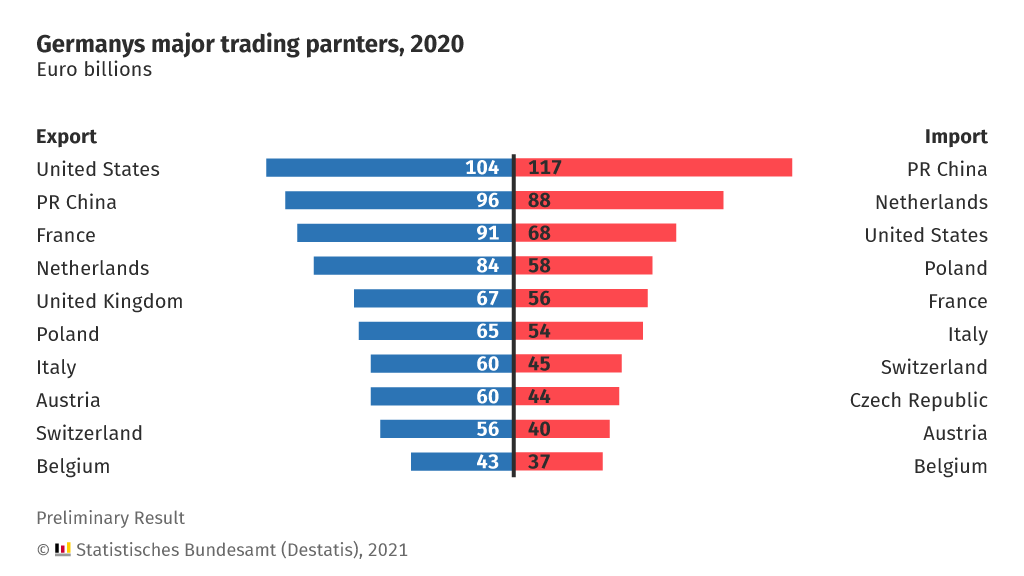
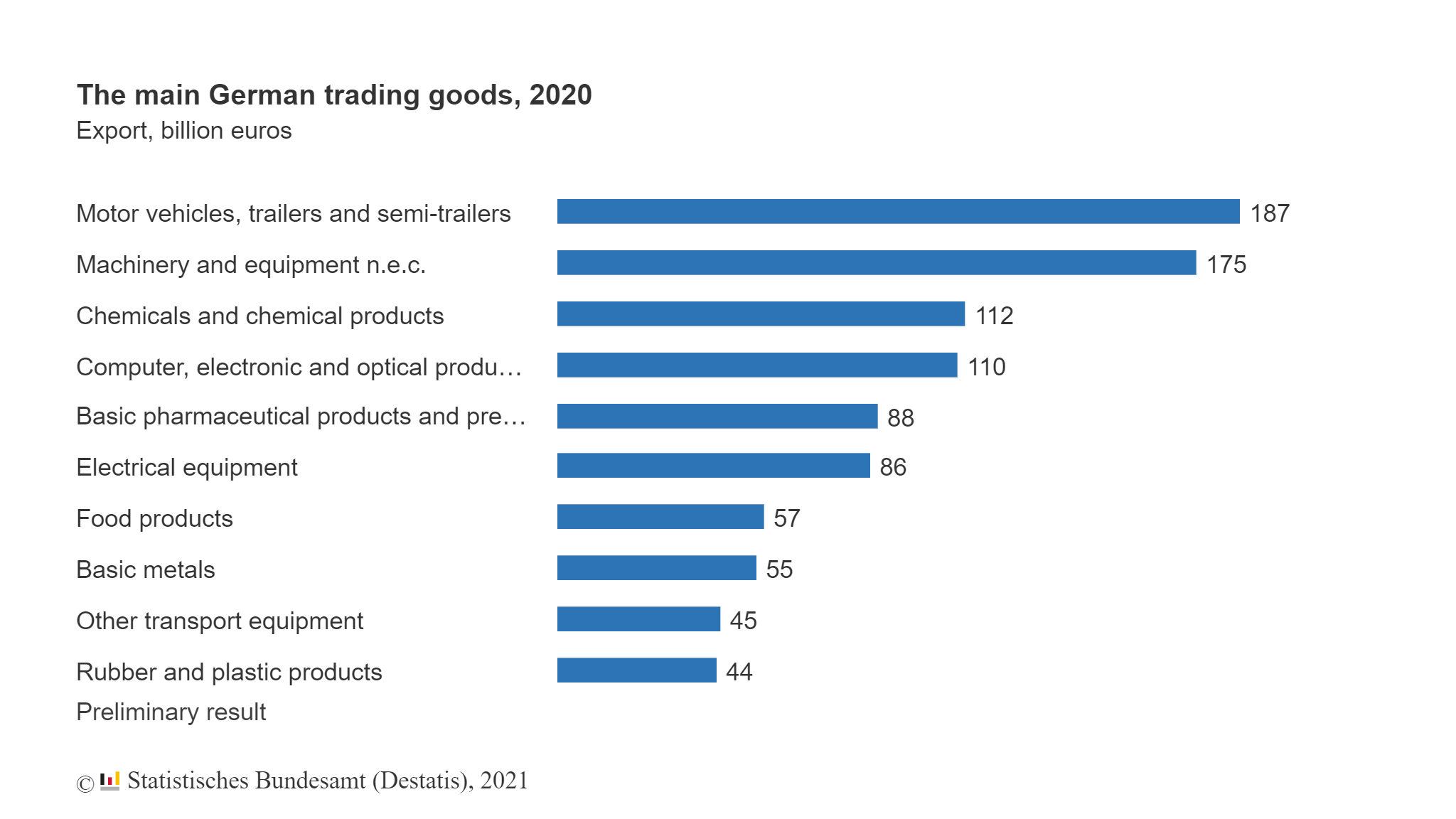
One of the great accomplishments of the British Empire in terms of infrastructure development projects was the construction of the “Main Line” railway line in Sri Lanka. The rail line was primarily built to transport tea from plantations efficiently to the ports for export to the UK and beyond. The following is a great documentary about this great railway line from Deutsche Welle.
Source: YouTube