The Singapore equity market has declined strongly due to the slowdown in Chinese economy. Unlike other Asian economies, the city-state of Singapore is highly dependent on China.
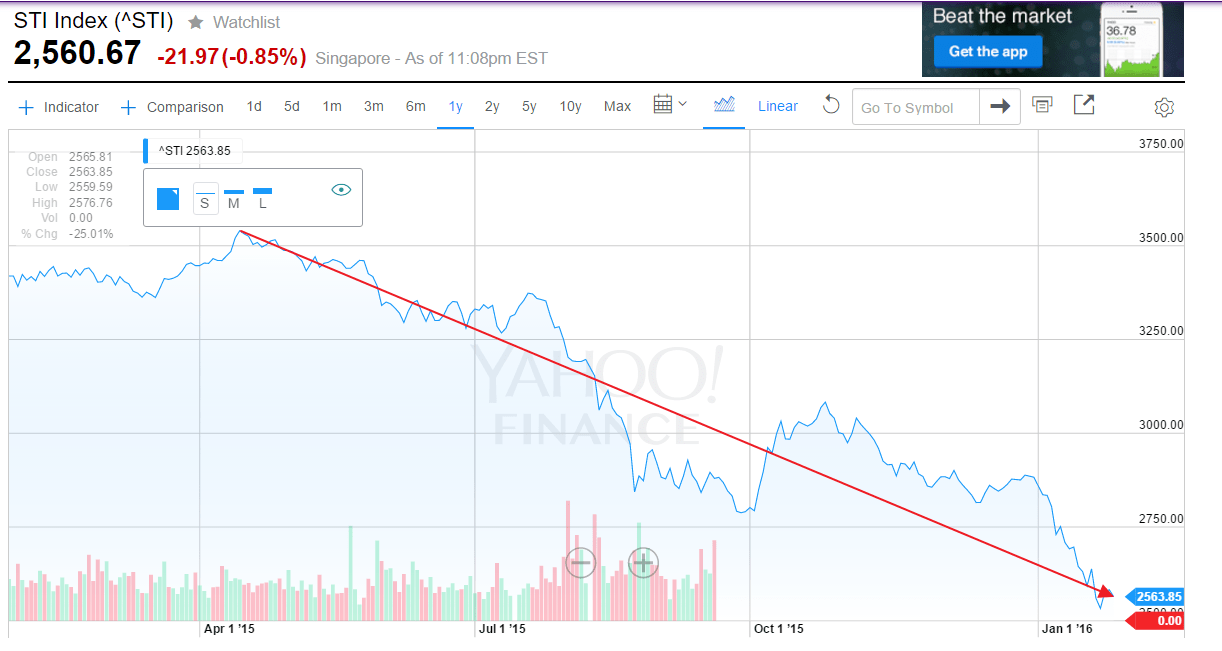
The benchmark Straits Times Index is down over 11% year-to-date. Over the past one year the index has lost over one-fourth of its value as shown below:
Click to enlarge
Source; Yahoo Finance
Here is a short excerpt on the trade relationship between Singapore and China:
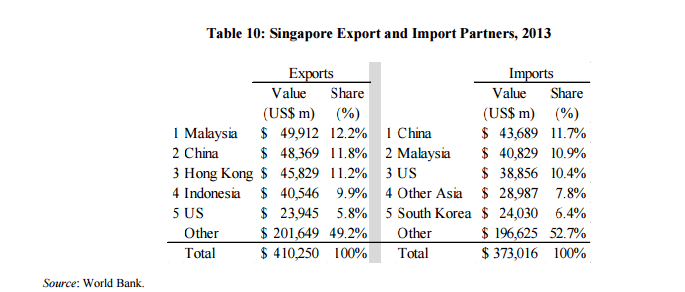
Though Singapore keeps a diverse portfolio of trade partners, China is its second-largest export and largest import partner (see Table 10). Malaysia is the other major trade partner, largely as a function of geographic proximity. The United States is Singapore’s fifth-largest export partner, accounting for nearly 6 percent of exports, valued at $23.9 billion.
Table 10: Singapore Export and Import Partners, 2013
Source: World Bank.
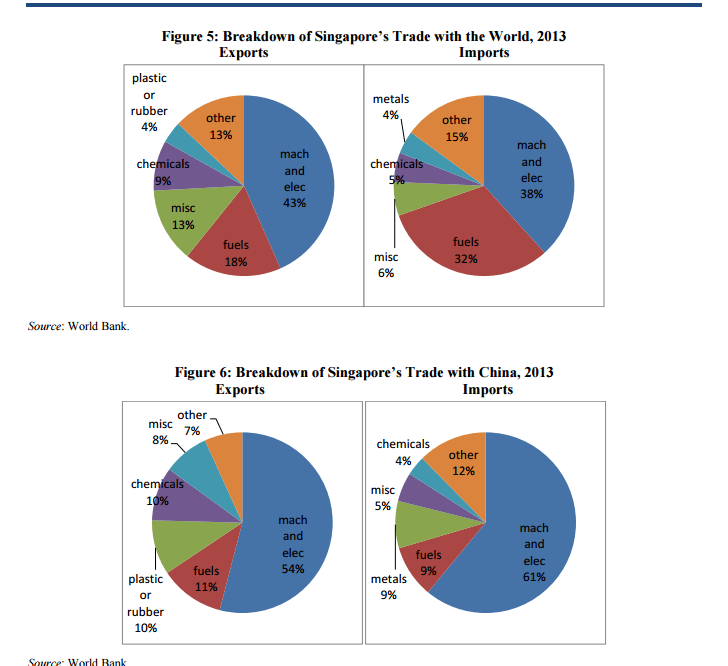
Due to Singapore’s role as an energy transit hub, about one-third of its imports and exports consist of fuels and petrochemicals (see Figure 5). These products, however, play less of a role in Singapore’s trade with China, over half of which—on both the export and import sides—consists of machinery and electrical products (see Figure 6), mirroring Singapore’s overall trade composition.
Source: China’s Economic Ties with ASEAN: A Country-by-Country Analysis, U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission
Following the overall Singapore market, the iShares MSCI Singapore ETF (EWS) has lost over 18% year-to-date and over 29% in one year.
Two of the largest Singapore banks – DBS Group Holdings Ltd (DBSDY) and United Overseas Bank Limited (UOVEY) have also fallen in line with the market. Unlike other countries Singapore does not charge withholding taxes on dividends paid out to foreign investors.The full list of Singapore ADRs can be found here.
Disclosure: No Positions