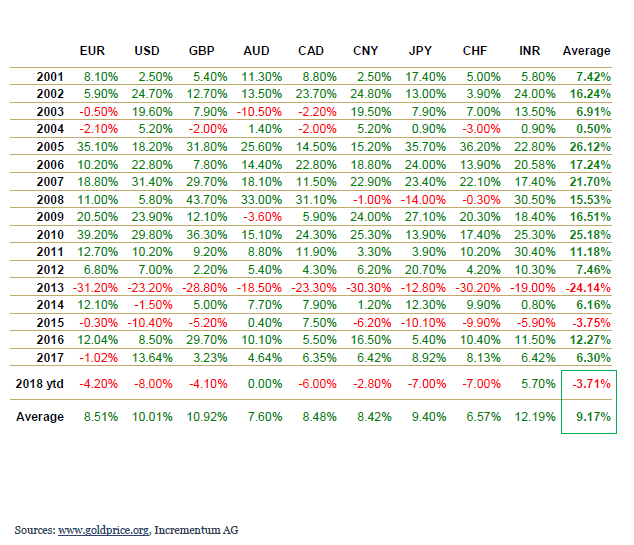
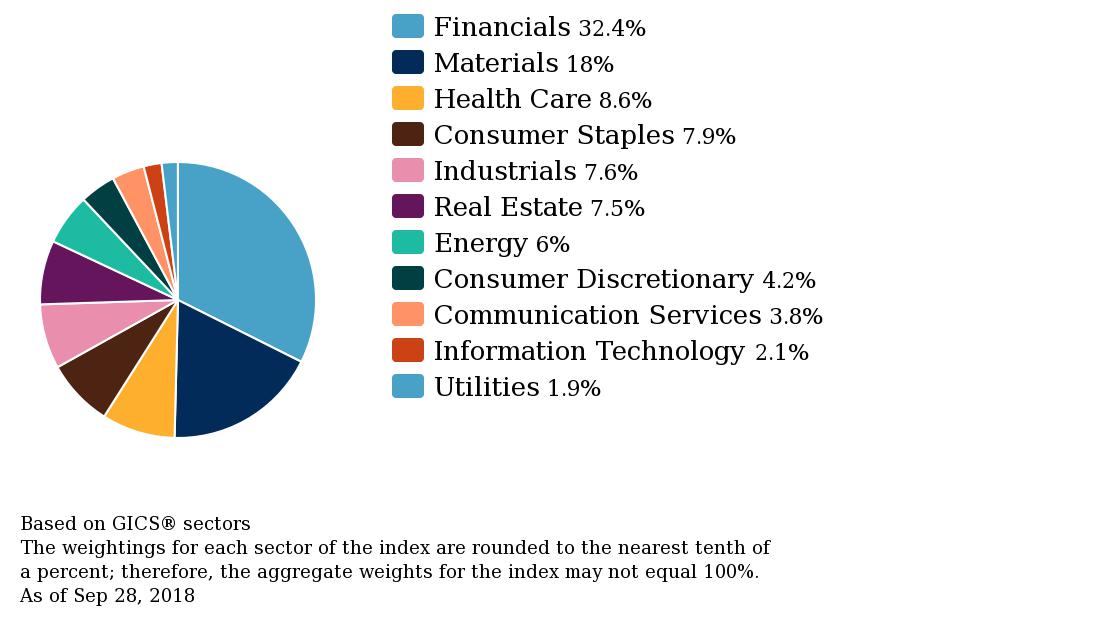
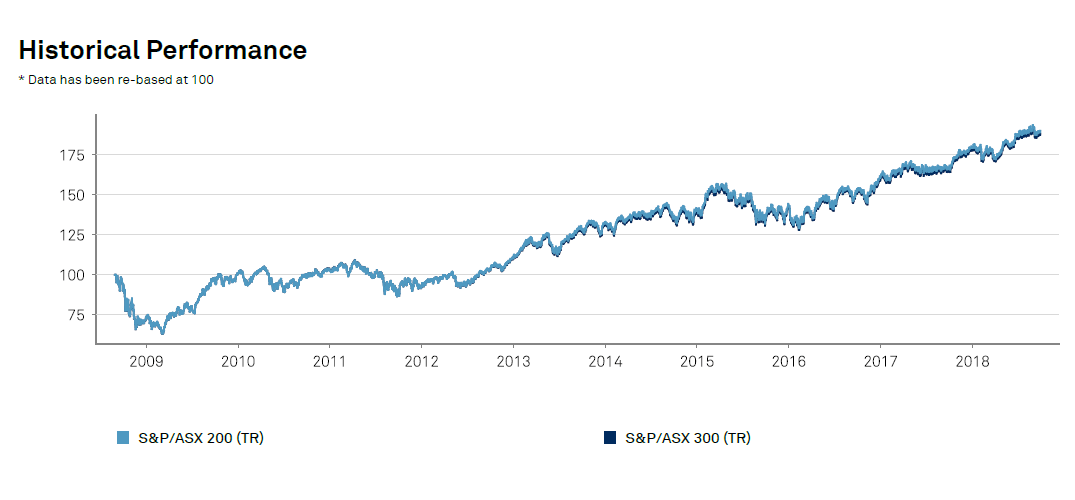
Gold prices are down so far this year. However gold as an asset class has returned positive returns in various currencies from 2001 thru 2017.
The performance of gold in various currencies is shown in the table below:
Click to enlarge
Source: IGWTreport, Incrementum
The average annual performance of gold between 2001 and 2017 was 9.17%. During period gold has outperformed practically every other asset class in particular in every currency according to the above linked report.
Download:
- In Gold We Trust Report 2018 (in pdf)