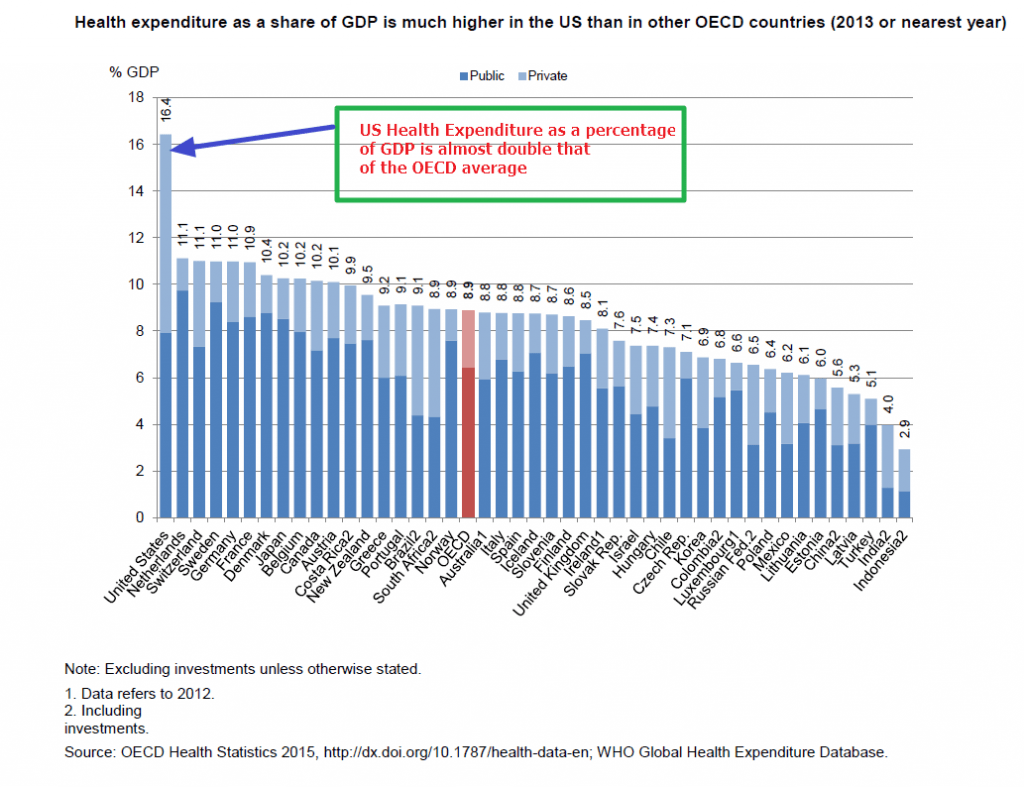
Health Care Expenditure in the US as a share of GDP is the highest among OECD countries according to the Heath at a Glance 2015 report by the OECD. Some of the key findings from the report are listed below:
- Life expectancy in the US is lower than in most other OECD countries due to several reasons including poor health-related behaviors such as drinking, obesity, etc. and the fragmented healthcare system in the country. Life expectancy in the US is 78.8 years in the US in 2013 compared with 80.5 years for the OECD average. In 1970 the US rate was one year higher than the OECD average. The growing gap between the US and other countries is due to many reasons, including prevelance of important risk factors to health and the fragmentation of the healthcare system with little resources devoted to public health and primary care.
- The proportion of adults who smoke in the US is the lowest in OECD countries but alcohol consumption is rising and obesity rate is the highest. The rate has declined from 33.5% in 1980 to 14% in 2013.
- The quality of acute care in hospital in the US is excellent. However the US health system is not performing well in avoiding admissions for people with chronic diseases.
- Obesity rates among adults in the US are the highest among OECD countries, with 35% of adults being obese. Obesity is a known factor for many health problems.
The following chart shows that health spending in the US still far exceeds other OECD countries:
Click to enlarge
From the report:
Although health spending growth has slowed down considerably in recent years in the United States, it remains much higher on a per capita basis than in all other OECD countries, and was two-and-a-half times greater than the OECD average in 2013. The share of GDP allocated to health spending in the United States (excluding capital expenditure) was 16.4% in 2013, compared with an OECD average of 8.9%. This share has remained unchanged since 2009, as health spending growth matched economic growth.
Source: OECD
Related:
- Health Care Spending Comparison Across OECD Countries (Year 2010 post)
- US obesity rates ‘rising for first time since 2004 (BBC)