Investing in a foreign stock is not as easy as selecting a company and placing a buy order as one would with a US stock. After an investor has decided to invest in a foreign stock, there are usually three different options to trade the stock.
For example, lets say an investors has decided to invest in Diageo plc, the UK-based global liquor maker. The company’s equity is traded as ordinary stock on the LSE (DGE.L), as ADR on the NYSE (DEO) and also as foreign ordinary on the OTC market (DGEAF) in the U.S. So the investor has to consider various factors to determine the best option suitable to invest in Diageo stock.
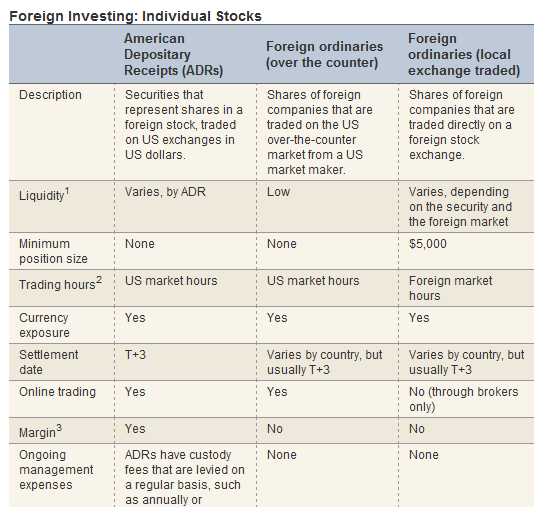
The following table lists the advantages and disadvantages of the three options:
Source: Going Global: Selecting ADRs or Foreign Stocks, Schwab Center for Financial Research
Key points
1.ADRs are suitable for smaller positions, have decent liquidity, can be traded online during US market hours, and are generally marginable.
2.Foreign stocks listed in the US OTC market are an alternative for smaller positions, however costs tend to be higher than ADRs and the liquidity may not be as strong.
3.Foreign stocks listed in the local market are often the best alternative for orders greater than $5,000, due to their superior liquidity and costs.
It must be noted that not all foreign stocks may have all the three options. Some foreign companies may trade only on the OTC markets (either as an ADR or as an ordinary) since listing on the NYSE is expensive and places many regulatory burden on these companies. Foreign companies trading on the OTC market are not just small and unknown firms. In fact, many large foreign multinationals such as Nestle (NSRGY) trade on the OTC market for the reasons noted above. So though the OTC market may not be very liquid for small and long-term investors it may not be an issue.
Disclosure: No Positions